2. Hilda Theophila Lagerheim – a “stiftsjungfru”
Little Hilda Theophila Lagerheim was not yet a year old when her name appeared in the daily newspaper in Stockholm. Her name was listed among others – all girls of noble families. The announcement stated that the Board of the House of Nobility on the 2nd of May had accepted the applications of these girls to become maidens of the Vadstena Adliga Jungfrustift. Hilda, still a toddler, now had the title of Stiftsjungfru.
Before getting into the significance of this title, let’s first get back to the birth and childhood of Hilda.
Hilda was born on June 4, 1827. Her father, Olof Johan Lagerheim, was a nobleman and a Supreme Court Justice (thus Hilda’s ranking as 2 of all the 92 girls who were confirmed in St Jacob’s Church in May of 1844). Her mother was Emerentia Frigell, the daughter of a wholesale merchant.
When Hilda was born, the family lived in a wing behind the House of Nobility in the Old Town of Stockholm. The wing was later torn down and today there are two separate houses that serve as wings to the main building.
A few weeks ago, I wrote about another girl in the confirmation class, Therese Gustafva Aspegrén, and how her mother had died in the cholera epidemic of 1834. She also lived in Old Town and not too far from Hilda. The horrors of the epidemic affected them all. Therese’s mother had died on the 13th of September. Hilda’s father died from cholera 4 days earlier, on the 9th. That someone of his eminence would succumb to this disease was so sad, disconcerting, and surprising:
Among more familiar and prominent people who died of cholera was … Justice Olof Johan Lagerheim, an excellent official who was equally valued and liked for his humanity. Lagerheim was extremely active as chairman of his parish’s health committee. To set a good example and to encourage the townspeople, he volunteered to drive the carriage that collected the dead. He fell victim himself and succumbed to the disease from which he had managed to save so many of the congregation’s members. http://runeberg.org/gsthlm/0204.html
The family now had to move, and they moved to a house just a block away from St Jacob’s Church. Hilda’s mother was suddenly a widow at the age of 43 and had 6 children to care for: Ture 16, Louise 15, Nils 12, Carl 10, Hilda 6, and Johanna 3 years old.
Ten years later, in 1844, when Hilda was studying for her upcoming confirmation, the family still lived at this address. But now the mother had become ill. She had developed gangrene and there were no effective treatments for the disease. On the 24th of April, she died and the children became orphans. The funeral was at St Jacob’s Church one week before Hilda’s confirmation.
Vadstena Adliga Jungfrustift
So what was Vadstena Adliga Jungfrustift (Vadstena Noble Maiden Diocese) and what did it mean to have a title of Stiftsjungfru?
Vadstena is a picturesque town in Sweden, famous for its medieval Birgittine Convent and castle.
During the renaissance, noble families in Europe looked to convents for educating and supervising their daughters until they were ready for marriage. Unmarried noblewomen and widows whose families were unable to care for them were also in need of financial help and a place to live.
After the reformation, catholic convents were not an option for the protestant noble families. Instead, they started protestant “convents”, so-called jungfrustift for unmarried women of noble families. Jungfru, literally “young woman”, refers to a maiden and stift means a diocese. A woman belonging to a jungfrustift was given the title stiftsjungfru, literally, “diocese maiden”.
There were jungfrustifts in Germany and Denmark. In Sweden, there were two – the one in Vadstena, which started in 1739, and one in Norrköping (1783-1796).
The one in Vadstena had lofty goals and got the King’s permission to use the castle to house the women. The estimated cost of running this convent, however, was prohibitive and in the end, the organization moved to Stockholm and became a simple pension fund in 1822, managed by the House of Nobility.
Vadstena Adliga Jungfrustift still exists. Parents will apply for their daughters when they are young, just like Hilda’s parents did. Today, noblewomen can also apply by themselves. There is a small application fee. To be eligible for the pension, the woman has to be single or a widow. Today, the number of women getting a yearly pension is capped at 100. These are the 100 women with the longest membership.
These rules must have changed, as Hilda, who was still young, received a pension from the fund as published in the daily newspaper. On May 6, 1865, she was listed among those who received 50 RKS RMT yearly; the other cohort received 100. Hilda’s pension would be equivalent to 3500 SEK today, or $424.
What happened to Hilda after 1844?
Who took care of Hilda and her siblings after they became orphans? The year was 1844 and the following year, no one in the family lived at their old address. Hilda seems to have disappeared from all digitized church and census records in Stockholm. Some of Hilda’s siblings appear in those records, but not Hilda.
So instead, I search for her in the digitized daily newspapers. And that is where I find the announcements of Vadstena and her pension. And I find her obituary and an advertisement about the subsequent auction of all her belongings. The auction mentions an address – Sjöberg’s Bookstore in the town of Västerås. Would they really have hauled all her things to a bookstore? Then it hits me that maybe she lived in the same house as the bookstore? I check the church records – the pastor’s house examination book, where he yearly checked on each household and made sure they knew how to read and that they knew their bible. And there, I find her name! She is indeed living with the Sjöberg family and now I can and go backward in time through volumes of church records – all her moves from place to place, parish to parish, neatly (or sometimes illegibly) penned down by pastors. It takes me a week to find the crumbs she left behind as she moved around Sweden.
This is her story, but now in chronological order, starting with the year she left Stockholm.
Häringe Castle
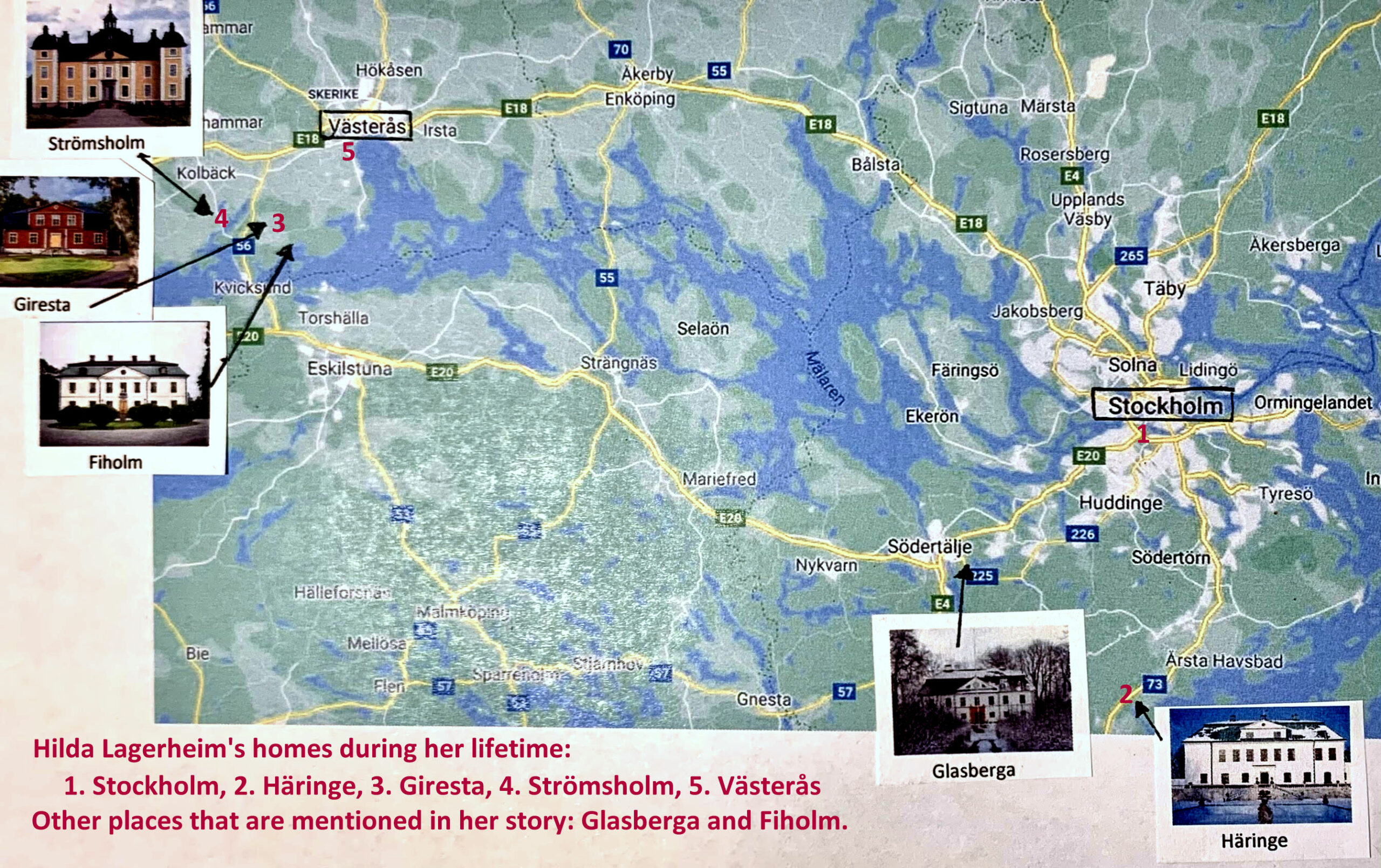
In 1848, Hilda is 21 years old. She moves from Stockholm to Häringe Castle in Västerhaninge parish.
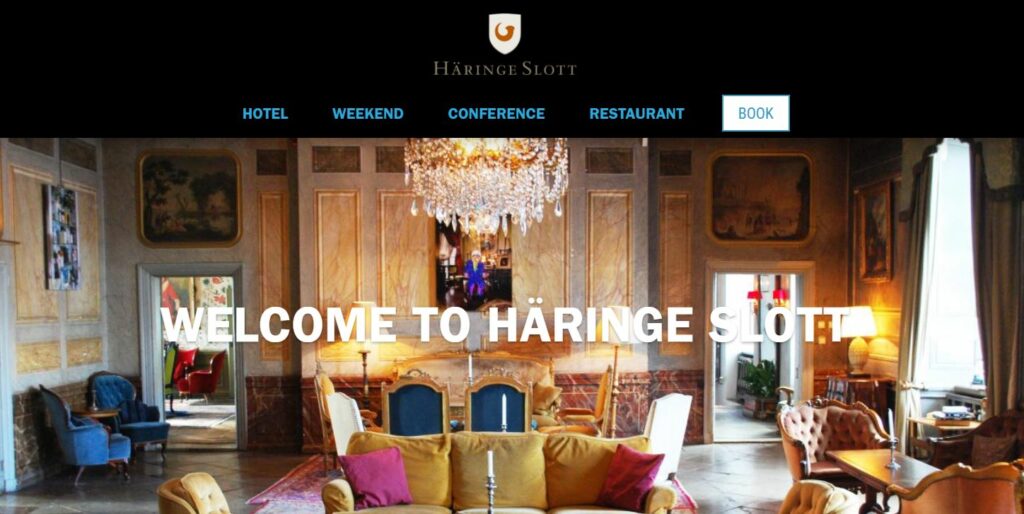
Häringe Castle. Today it is a hotel. You can book it on Expedia and have a “yummy breakfast, poolside” as one guest wrote. Times have changed more than Hilda could ever imagine. But we can imagine Hilda sitting in this room some 170 years ago.
Häringe is a castle owned by Baron Axel Wilhelm Löwen (b. 1783). He is married to Lovisa Ehrensvärd (b. 1793). Together they have 5 daughters between the ages of 18 and 26. All the girls were born at an estate that the Löwen family also owned – Glasberga. What an interesting coincidence – my grandfather owned Glasberga manor when my dad was a toddler.
How did Hilda end up at Häringe? She obviously was not hired to be a governess to the daughters as they were all close to her in age.

Ulrika Elin Christina Löwen (b. 1822). One of the daughters in the family. Photo from the House of Nobility.
Could she have been invited to be a lady’s companion to the girls’ mother’s sister, Fredrika Ehrensvärd, who had recently moved in with the family? Or did the family know Hilda’s family and invited her to live with them?
In 1852, the mother, Lovisa Ehrensvärd dies. And in 1855, after 7 years at Häringe, the pastor writes in the house examination book that Hilda has moved away. I check the records of parishioners moving to another parish (that is how I can track her moves – records of moving in and out of parishes) but it simply states that she has been removed from the parish’s records. Where did she go?
Giresta in Rytterne Parish
According to the church records in Rytterne, Hilda is registered as moving into this parish in 1857. That is 2 years after she left Häringe. The records state that she came from Västerhaninge parish, which is correct. Did she go somewhere else for 2 years without registering with a parish?
She has now moved in with a family at an estate by the name of Giresta in Rytterne parish. Giresta is a farm that belongs to a larger estate – Fiholm. Again a surprise as it is a familiar name. My favorite aunt, Aunt Piggen (Marianne Ridderstolpe), was born and raised at Fiholm and I have a wonderful childhood memory of celebrating Midsummer there.
The family residing at Giresta is Baron Adolf Falkenberg (b. 1807) and his wife Eva Fredrika Skjöldebrand (b. 1815) and their 4 children.
Also residing at Giresta is a forester, Johan Fredrik Ludvig Kolbe (b. 1802), his wife Gustafva Hedvig Catharina Rudbeck (b. 1824), and her sister, Fredrika Helena Charlotta Rudbeck (b. 1828).
Interestingly, Forester Kolbe is the brother of Carolina Kolbe, the wife of Fredrik Ridderstolpe (b. 1783) who is the owner of Fiholm and Giresta. In 1861, Forester Kolbe dies and Gustafva is now a widow. She, her sister Fredrika, and Hilda have to move.
Strömsholms Palace
In 1862, the three women move to a beautiful place – Strömsholm in Kohlbäck parish. Strömsholm is a royal palace and has been an equestrian center since the 16th century.
According to the church records, Hilda and the two sisters Rudbeck rent rooms in the house of the palace chamberlain, N.G. Eek. Again, why did they move here? Three young women from noble families.
In December of 1864, Hilda is in the papers again. This time, an upper court has decided that Hilda will not be entitled to managing her own affairs, but to still have a guardian, even though the law has just changed to grant women majority at the age of 25.

What does that mean? Why was she not trusted to take care of herself? And who was her guardian? One of her brothers? Had her guardian brought her case to court or had she requested to still have a guardian? If you had had a guardian taking care of you all your life, not having one might be frightening. A guardian would be responsible for you and make sure you were taken care of.
Hilda and her friends live at Strömsholm for 6 years until 1868, when it is time to move again. And this time, they take two of their maids with them.
Västerås
Västerås is a provincial capital and now, Hilda will be living in a town again. Maybe that was exciting. Hedvig, who is a widow, marries a bookstore owner, Carl Magnus Sjöberg on the 12th of June 1870.
Two years later, on February 26, 1872, at an age of 44, Hilda dies from chronic pneumonia and acute lung edema. The following August, there is an auction of the belongings, listed as furniture, various household items and other things, and even a hooded buggy.
To keep her life story straight, I found that I had to construct a map to get an idea of the places where she had lived.
Hilda’s Siblings
So what happened to Hilda’s siblings?
Ture, the oldest brother, never married and died from a stroke at age 33.
Johanna, her younger sister, also did not marry and died from gastric fever at the age of 27.
Then there was Carl who also did not marry but was a lawyer and worked for the court (Svea Hovrätt) that had decided that Hilda should still have a guardian. Was he her guardian? Carl died in Bellagio in Italy where he was staying to cure an illness. He was 58.
Nils married and had children.
And then there was Louise, Hilda’s older sister. She married Jakob von Knorring, had children, and was a very accomplished artist and musician.
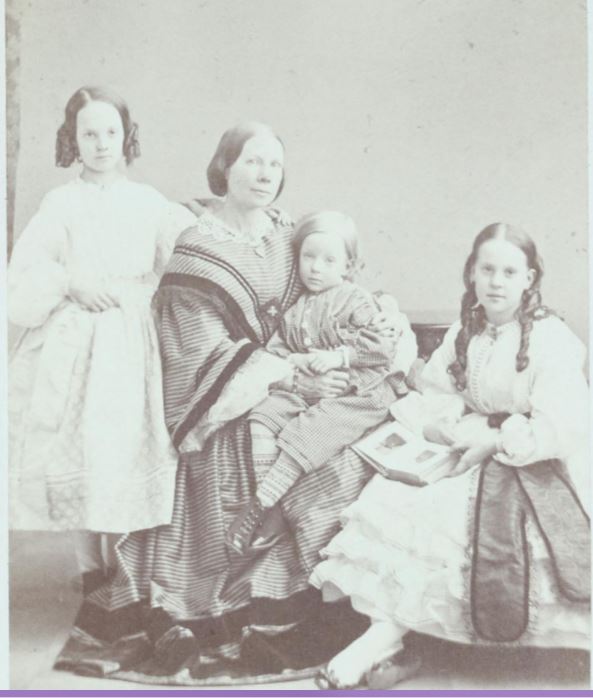

Hilda’s older sister, Louise Emerentia Lagerheim, married von Knorring, with her 3 children: Augusta Emerentia Amalia, Sigrid Elisabeth Lovisa, and Egenolf Alexander Elias. Photo from the House of Nobility.







[…] 2. Hilda Theophila Lagerheim […]
[…] The parents of two other friends of Augusta and Cecilia also died from cholera that fall, Therese Gustafva Aspegrén and Hilda Theophila Lagerheim […]
[…] The parents of two other friends of Augusta and Cecilia also died from cholera that fall, Therese Gustafva Aspegrén and Hilda Theophila Lagerheim […]
[…] The parents of two other friends of Augusta and Cecilia also died from cholera that fall, Therese Gustafva Aspegrén and Hilda Theophila Lagerheim […]